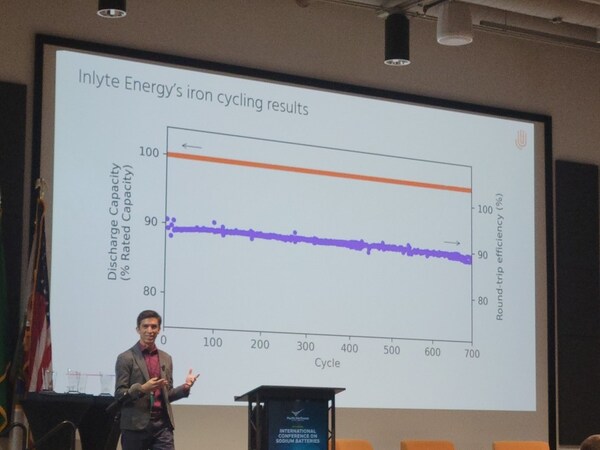
Big-battery storage capacity could increase fivefold in Germany by 2026
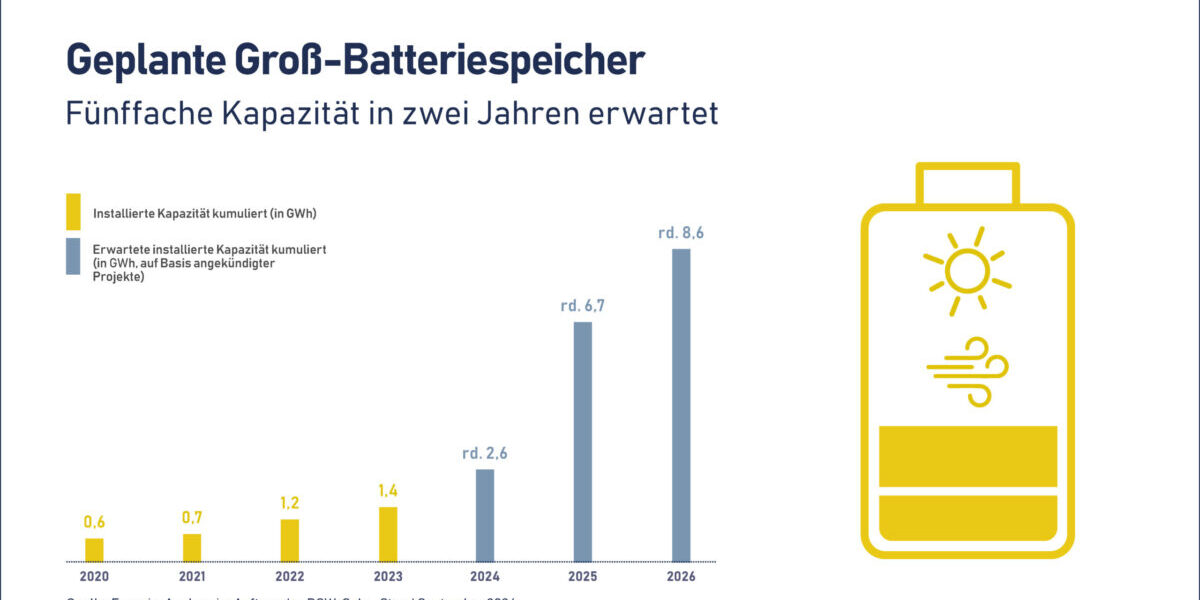
German solar trade body BSW-Solar expects the capacity of large battery storage systems installed in Germany to increase fivefold by 2026.
With 1.8 GWh of capacity installed to date, in systems with at least 1 MW of connected capacity, BSW-Solar expects around 7 GWh will be added by 2026, according to analysis by Enervis on behalf of the membership body. Enervis considered pre-registered projects in the market master data register as well as company announcements.
Enervis found 1.51 million home storage systems were installed by the end of June 2024, with a total capacity of around 13 GWh, and around 1.1 GWh of commercial battery storage capacity was also present, for just under 16 GWh of storage capacity in Germany at the end of June.
Solar generation capacity is outpacing storage additions, with more than 90 GW of solar installed. On sunny days, electricity prices plummet and systems have to power down to ease grid constraints.
BSW-Solar said legislative obstacles to the construction and operation of storage systems must be removed to accelerate deployment and smooth the integration of renewables into Germany’s energy mix.
For example, a temporary exemption from double electricity network charges applied to stored power must be made permanent by the Federal Network Agency, BSW-Solar says.
The association has also proposed battery storage system privileges be included in a forthcoming amendment to Germany’s building code, to bring the technology in line with other energy transition equipment.
The current expansion in German large-scale energy storage is being driven by electricity market dynamics, with batteries profiting from differences between high and low electricity prices which are linked to periods of demand.
“The [electricity-]price-reducing feed-in of more and more solar power makes the increasingly cheaper storage of electricity an interesting business model,” said Carsten Körnig, chief executive of BSW-Solar.
He called for swifter roll-out of large-scale storage as part of a drive to reinforce a grid which is having to accommodate ever-more variable-generation renewables.
“Large battery storage facilities should be expanded more quickly as an ideal systemic addition to solar and wind energy in order to make the supply more consistent and even more reliable,” added Körnig. “This will allow the generation and consumption of electricity to be better balanced and avoid generation peaks that burden the grid. The aim must be to make sensible use of generation peaks from solar and wind power plants, with flexible consumers, battery storage systems, and electrolyzers, instead of simply regulating the systems.”
From pv magazine Deutschland.