World’s largest compressed air energy storage project breaks ground in China
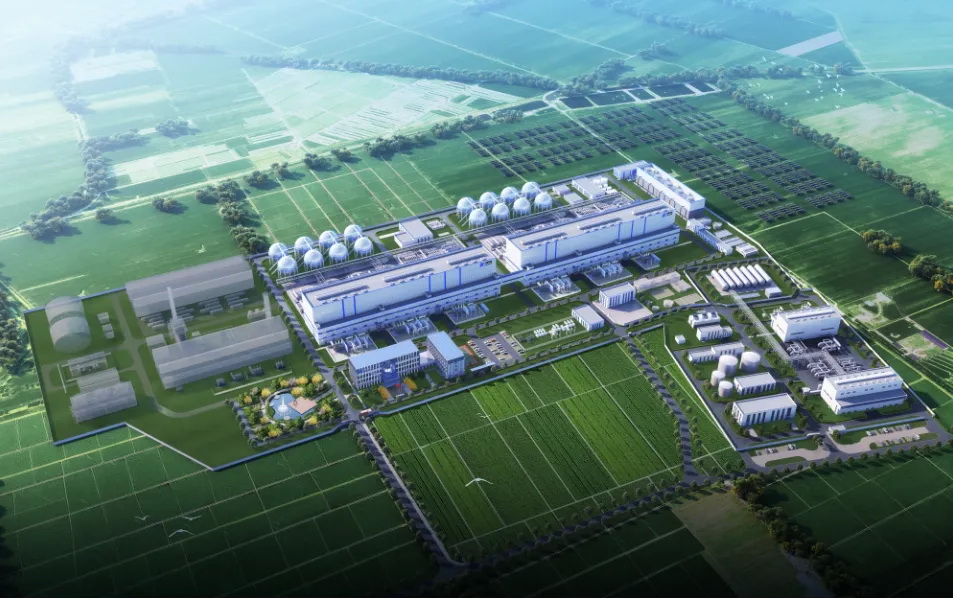

China’s Huaneng Group has launched the second phase of its Jintan Salt Cavern Compressed Air Energy Storage (CAES) project in Changzhou, Jiangsu province, in a new milestone for the global energy storage sector. Once completed, the project will hold the title of the world’s largest compressed air energy storage facility, integrating groundbreaking advancements in both power output and efficiency.
Phase two of the project will feature two 350 MW non-fuel supplementary CAES units, with a total storage volume of 1.2 million cubic meters. This scale makes it the largest single-unit power generation capacity, total storage capacity, and integrated efficiency of any CAES facility worldwide. The plant’s storage capacity will allow for up to 2.8 GWh of electricity per full charge, with an estimated annual 330 charge-discharge cycles.
The first phase of the Jintan project, completed earlier, saw the installation of a 60 MW CAES unit, offering valuable operational experience and laying the groundwork for the more advanced second phase.
The Jintan project is a collaboration between three entities. These include Huaneng International Power Jiangsu Energy Development Co., a subsidiary of Huaneng Group, which plays a central role in the investment, construction, and operation of the project. China National Salt Industry Group (CNSIG), through its subsidiary China Salt Cavern Comprehensive Utilization Co., provides underground gas storage capabilities that are key to the project’s feasibility, while Tsinghua University is a key R&D partner on the project.
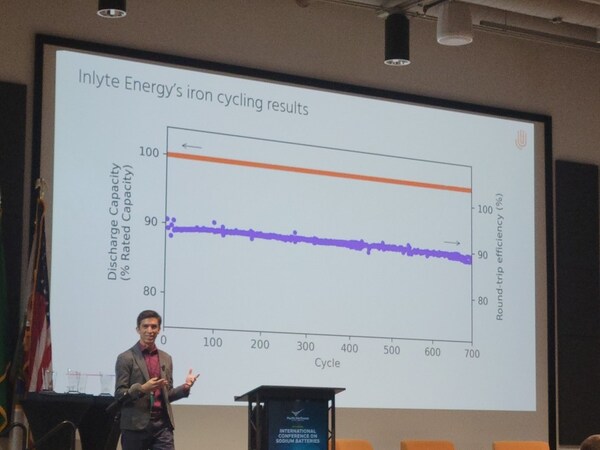
The Jintan project utilizes several innovative technologies that significantly enhance its efficiency. One standout feature is the non-fuel supplementary technology, which eliminates the need for external fuel sources in the energy generation process. Instead, the heat produced during the compression of air is stored and reused, achieving zero carbon emissions and an energy conversion efficiency of over 60%.
Additionally, the project has optimized the energy storage system integration, refining the process flows and equipment configuration to improve overall performance and reliability. The facility also features an innovative “one-click start” control system, streamlining operations for staff and reducing startup times. The machine efficiency has increased by 0.5%, and the air turbine quick-start method has reduced generator startup times from 20 minutes to just 5 minutes, boosting both peak-shaving response speed and operational efficiency.