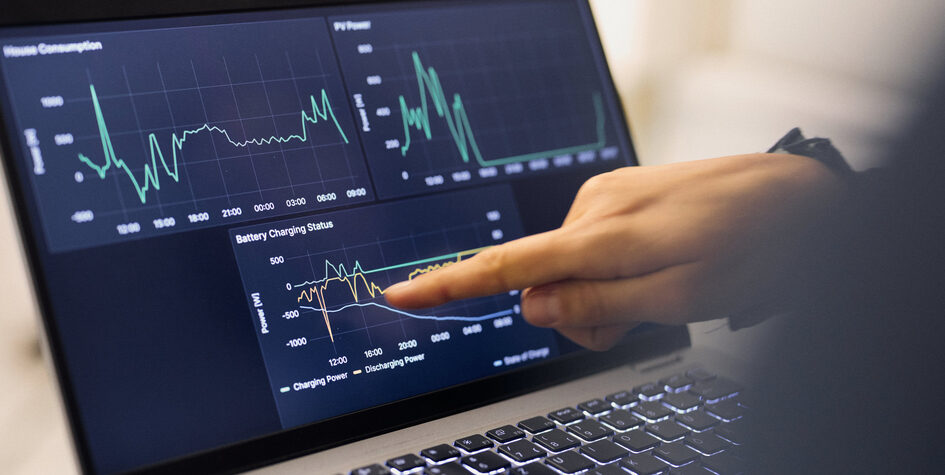
R&D
Advertisement
Advertisement
Advertisement
Latest News
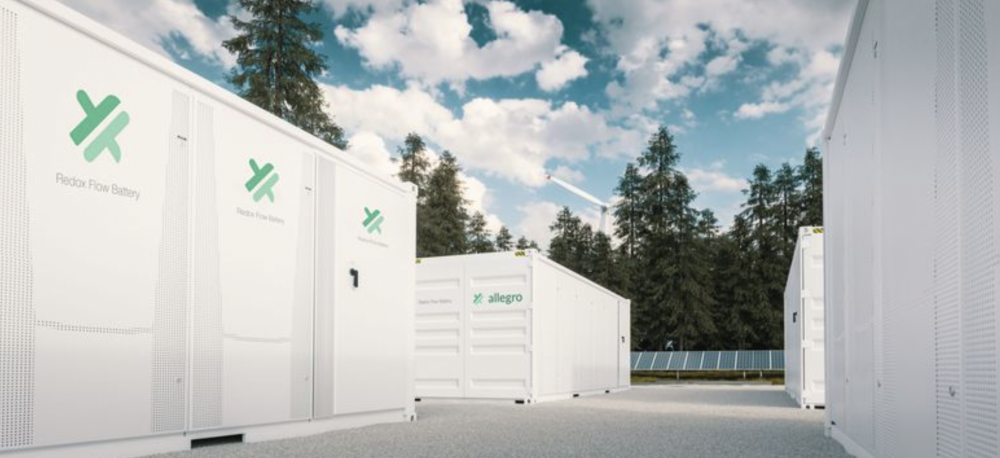

Australian redox flow water-based battery developer lands state grant
Allegro Energy has secured a AUD 2.1 million ($1.3 million) grant from the New South Wales state government to develop an Australian-made, aqueous-based redox flow battery energy storage prototype capable of storing energy for more than 10 hours.
Dec 20, 2024
Advertisement
All R&D news

Storing solar energy as heat in synthetic molecules for future energy storage systems
German researchers are testing lab-made molecules designed to absorb, store, and release solar energy on demand, acting as 'heat batteries'. The researchers say their method is more efficient at storing solar energy compared to conventional thermal heat storage systems.
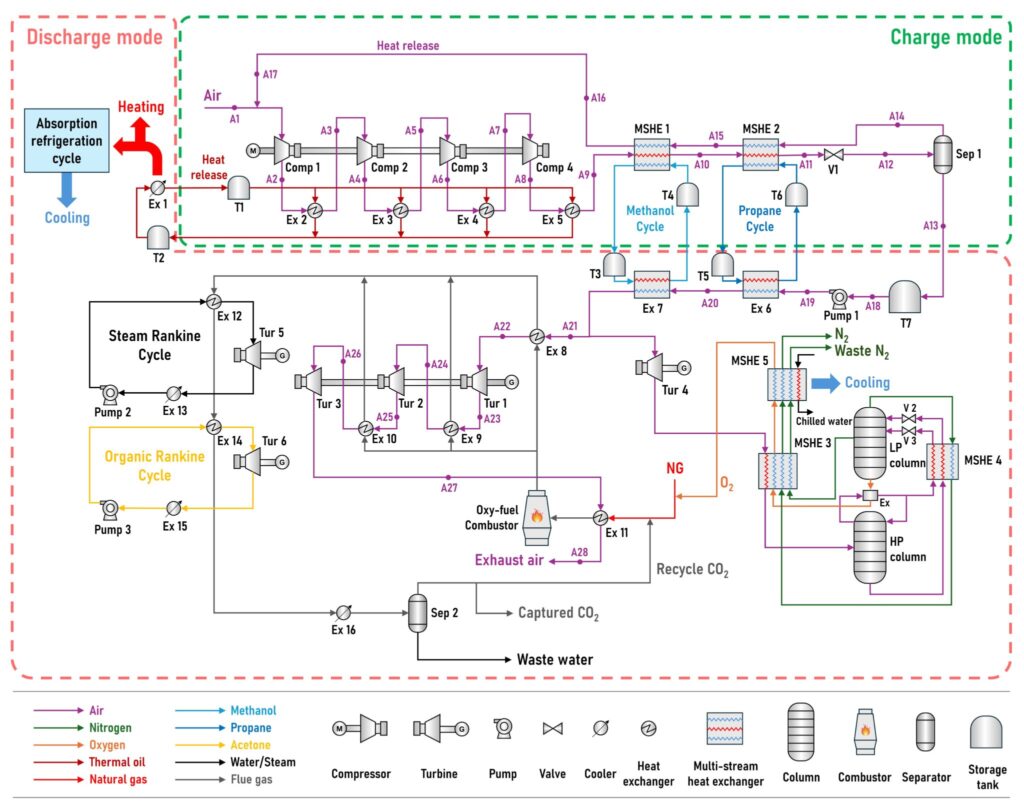
New standalone liquid air energy storage system concept beats conventional system with efficiency boost
Korean scientists have designed a liquid air energy storage (LAES) technology that reportedly overcomes the major limitation of LAES systems – their relatively low round-trip efficiency. The novel system enhances efficiency by increasing power output through the generation of thermal energy using natural gas as the external fuel during energy release.
Advertisement
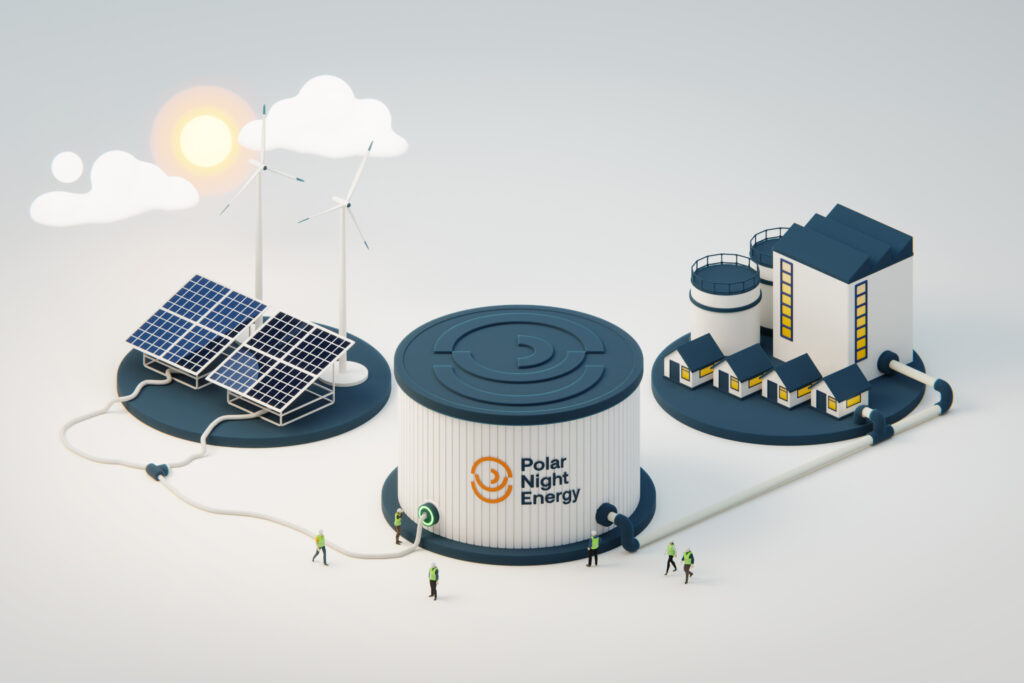

Testing to start on 100 MWh sand-based thermal battery in Finland
Finnish startup Polar Night Energy is building an industrial-scale thermal energy storage system in southern Finland. The 100-hour, sand-based storage system will use crushed soapstone, a by-product from a fireplace manufacturer, as its storage medium.

Hitachi achieves headway with first UK intercity battery train trial
The trial in the north of England has demonstrated that a 700 kW battery can enable quieter, zero-emission travel in and out of non-electrified stations. During the tests, a train was recorded operating solely in battery mode for 70km, a sufficient distance to cover bridges, tunnels, and stations.
Advertisement
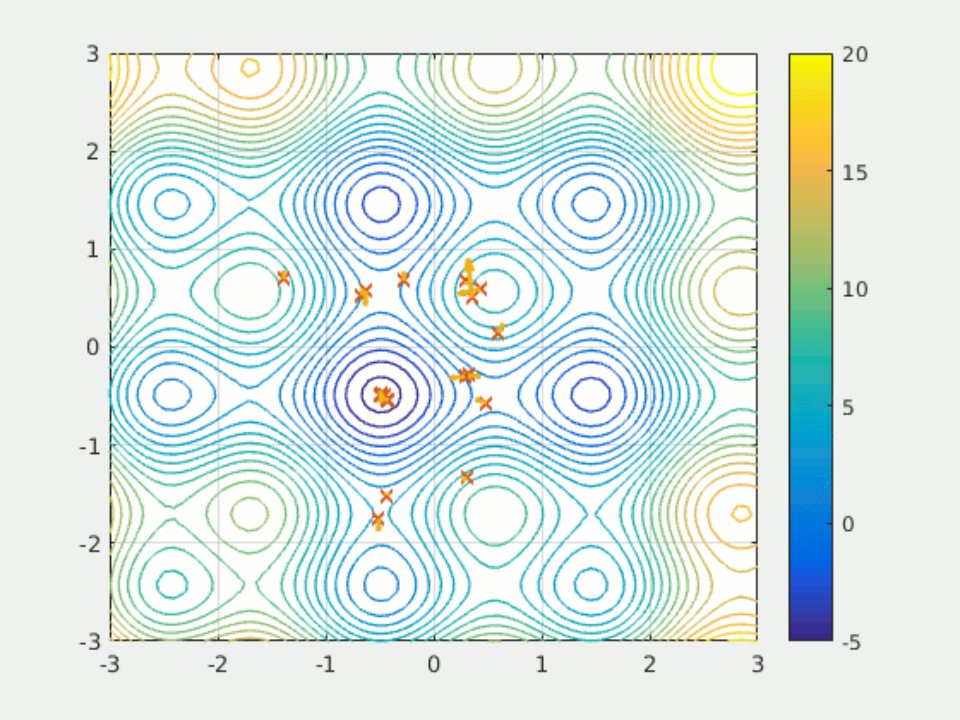
New grid forming strategy for solar batteries
Scientists from a major Chinese grid operator have proposed to use an enhanced version of the particle swarm optimization algorithm to adjust inertia and damping coefficients in batteries linked to PV systems. Their approach was validated through a series of simulation and was found to enhance transient performance.
Advertisement